
Contributing to an IRA is a smart move. There are two major varieties for the typical taxpayer to take advantage of: Traditional or Roth. The Traditional IRA gives you a tax deduction on contributions, while the Roth IRA lets you take distributions from the account in retirement without paying taxes.
They are both excellent tools to help you build a substantial portfolio enabling you to support yourself when you can no longer work.
I highly recommend you use one or both to help you save for retirement today.
But there are income limits that might affect your ability to use these accounts to the fullest. And these limits change each Fall (for instance, here’s the 2023 announcement from the IRS). Let’s look at each one closely.
Historical Traditional IRA Income Limits
For those who participate in their employer’s retirement plan:
| Year | Married Filing Jointly or Qualifying Widower | Married Filing Separately (lived with spouse) | Single, Head of Household, or Married Filing Separately |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $116,000 - $136,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $73,000 - $83,000 |
| 2022 | $109,000 - $129,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $68,000 - $78,000 |
| 2021 | $105,000 - $125,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $66,000 - $76,000 |
| 2020 | $104,000 - $124,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $65,000 - $75,000 |
| 2019 | $103,000 - $123,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $64,000 - $74,000 |
| 2018 | $101,000 - $121,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $63,000 - $73,000 |
| 2017 | $99,000 - $119,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $62,000 - $72,000 |
| 2016 | $98,000 - $118,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $61,000 - $71,000 |
| 2015 | $98,000 - $118,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $61,000 - $71,000 |
| 2014 | $96,000 - $116,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $60,000 - $70,000 |
| 2013 | $95,000 - $115,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $59,000 - $69,000 |
| 2012 | $92,000 - $112,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $58,000 - $68,000 |
| 2011 | $90,000 - $110,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $56,000 - $66,000 |
| 2010 | $89,000 - $109,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $56,000 - $66,000 |
| 2009 | $89,000 - $109,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $55,000 - $65,000 |
| 2008 | $85,000 - $105,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $53,000 - $63,000 |
| 2007 | $83,000 - $103,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $52,000 - $62,000 |
| 2006 | $75,000 - $85,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $50,000 - $60,000 |
For those who DO NOT participate in their employer’s retirement plan:
| Year | Married Filing Jointly (Spouse Covered) | Married Filing Separately (Spouse Covered) | Single, Head of Household, Qualifying Widower, MFJ or MFS (Spouse Not Covered) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $218,000 - 228,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2022 | $204,000 - 214,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2021 | $198,000 - 208,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2020 | $196,000 - 206,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2019 | $193,000 - 203,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2018 | $189,000 - $199,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2017 | $186,000 - $196,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2016 | $184,000 - $194,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2015 | $183,000 - $193,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2014 | $181,000 - $191,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2013 | $178,000 - $188,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2012 | $173,000 - $183,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2011 | $169,000 - $179,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2010 | $167,000 - $177,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2009 | $166,000 - $176,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2008 | $159,000 - $169,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2007 | $156,000 - $166,000 | $0 - $10,000 | No Limit |
| 2006 | No Limit | No Limit | No Limit |
Historical Roth IRA Income Limits
Every year, the income limits are evaluated against inflation and incomes to determine if a change is needed. In the past ten years, there has only been one instance where the limit did not change for one of the two major categories.
| Year | Married Filing Jointly or Qualifying Widower | Married Filing Separately (lived with spouse) | Single, Head of Household, or Married Filing Separately |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $218,000 - $228,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $138,000 - $153,000 |
| 2022 | $204,000 - $214,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $129,000 - $144,000 |
| 2021 | $198,000 - $208,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $125,000 - $140,000 |
| 2020 | $196,000 - $206,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $124,000 - $139,000 |
| 2019 | $193,000 - $203,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $122,000 - $137,000 |
| 2018 | $189,000 - $199,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $120,000 - $135,000 |
| 2017 | $186,000 - $196,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $118,000 - $133,000 |
| 2016 | $184,000 - $194,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $117,000 - $132,000 |
| 2015 | $183,000 - $193,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $116,000 - $131,000 |
| 2014 | $181,000 - $191,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $114,000 - $129,000 |
| 2013 | $178,000 - $188,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $112,000 - $127,000 |
| 2012 | $173,000 - $183,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $110,000 - $125,000 |
| 2011 | $169,000 - $179,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $107,000 - $122,000 |
| 2010 | $167,000 - $177,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $105,000 - $120,000 |
| 2009 | $166,000 - $176,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $105,000 - $120,000 |
| 2008 | $159,000 - $169,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $101,000 - $116,000 |
| 2007 | $156,000 - $166,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $99,000 - $114,000 |
| 2006 | $150,000 - $160,000 | $0 - $10,000 | $95,000 - $110,000 |
Traditional IRA Income Limits for 2023
The IRS has chosen to limit your ability to fully deduct your contributions to a Traditional IRA based on your income. First, they split filers into two groups: those who are participating in a company retirement plan (i.e. 401K) and those who are not.
Once taxpayers are split into those two major categories, the IRS further refines the groups by filing status. In all cases, Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) is used to define income.
If you do participate in your employer’s plan and…
You file your taxes as Married Filing Jointly, or as a Qualifying Widower in 2023, your income needs to be below $116,000 for you to be able to fully deduct your contributions to a Traditional IRA.
- If your MAGI is between $116,000 – $136,000 then you are in the “phase-out” range and the amount you can deduct starts “phasing out.”
- At $136,000 you are unable to deduct the contributions you make to a Traditional IRA.
You file as Single, Head of Household, or Married Filing Separately (not living with your spouse) in 2023 your MAGI needs to be below $73,000 to completely deduct your contributions. Your phase-out range is between $73,000 and $83,000.
You file as Married Filing Separately (living with your spouse) in 2023, your MAGI needs to be $0. Your phase-out range is between $0 and $10,000.
You do not participate in your employer’s plan and…
If you file your taxes as Married Filing Jointly (and your spouse is covered by an employer plan) in 2023, your income needs to be below $218,000 for you to be able to fully deduct your contributions to a Traditional IRA.
- If your MAGI is between $218,000 and $228,000, then you are in the “phase-out” range and the amount you can deduct starts “phasing out.”
- At $228,000 you are unable to deduct the contributions you make to a Traditional IRA.
If you file as Married Filing Separately (and your spouse is covered by an employer plan) in 2023, your MAGI needs to be $0 to completely deduct your contributions. Your phase-out range is between $0 and $10,000.
If you file as anything else and your spouse (if you have one) is not covered under a plan, then have no income limits to your ability to deduct the contributions to your Traditional IRA.
Now let’s take a look at the Roth IRA and associated income limits. Thankfully, they are not as complex.
Roth IRA Income Limits for 2023
The IRS tax regulations limit your ability to contribute to a Roth IRA also by using your MAGI. They have three different categories based on your filing status.
If you file your taxes as Married Filing Jointly or a Qualifying Widower in 2023 then your income (specifically, your MAGI) needs to be below $218,000 for you to be able to fully contribute to a Roth IRA.
- If your MAGI is between $218,000 and $228,000 then you are in the “phase-out” range and the amount you can contribute starts “phasing out.”
- At $228,000 you are unable to participate in the Roth IRA.
Related: Excess Roth IRA Contributions: Does My Brokerage Keep Track of Income Limits?
For those who file as Single, Head of Household, or Married Filing Separately (not living with your spouse) in 2023, your MAGI needs to be below $138,000 to fully contribute. Your phase-out range is between $138,000 and $153,000.
Finally, for those of you who are filing Married Filing Separately (living with your spouse) in 2023, your MAGI needs to be $0. Your phase-out range is between $0 and $10,000.
More About MAGI and Contribution Limits
Want to know what your MAGI is? First, find your AGI. Check out your tax return. Your AGI is at the very bottom of page 1. It’s essentially your income minus your “above-the-line” deductions.
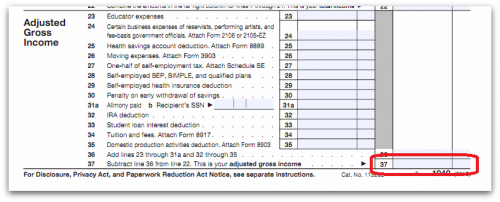
Now take that number and add back in your IRA deduction, student loan interest, tuition and fees deductions, any domestic production activities, any foreign earned income exclusions, any foreign housing deduction, any excluded qualified savings bond interest, and finally, any excluded employer-provided adoption benefits.
Thanks to Jim from Financial Ducks in a Row for explaining how to determine your MAGI.
Tax saving tip: Note that 401K contributions (which is a deduction you take to get to AGI) don’t get added back in to determine your MAGI.
Use this knowledge to your advantage. If you are close to reaching your phase-out limits then add more contributions to your 401K to drop your MAGI so that you can continue investing.
Are you wondering what it means to “fully contribute” to your IRA? In short, your 2023 contribution limit is $6,500 annually.
Those 50 and older can tack on an additional $1,000 for a total contribution of $7,500. For more on this, see the Traditional and Roth IRA contribution limits.
The post Traditional and Roth IRA Income Limits for 2023 appeared first on Part-Time Money®.
from Part-Time Money® https://ift.tt/lIcvBJK
Comments
Post a Comment
We will appreciate it, if you leave a comment.