The Capital Assets Pricing Model (CAPM):
The CAPM shows how the base-required return from stated security relies upon its risk.
Security whose profits are profoundly connected with variances in the market is said to have a significant level of systematic risk. It does not put a lot of risk-reducing potential on the investor’s portfolio.
Thus, generally, a high return is expected. On the other hand, a security with a low relationship with the market (low systematic threat) is significant as a threat minimizer. Thus its necessary return will be lower.
The proportion of the systematic risk of security comparative with that of the market portfolio is alluded to as its beta factor. In practice, industries such as construction are far more volatile than others, such as food retailing, and would have correspondingly higher betas.
The CAPM shows the direct connection between the risk premium of the security and the risk premium of the market portfolio.
The risk premium of share = market risk premium * ß
i.e. Required return of share = Rf + (market risk premium * B) or
E(r)i = Rf + Be(E(rm) – Rf)
If an investment is risk-free, then ß = 0.
The same formula can be applied to calculate the least required return of a capital funding project done by an organization.
To utilize the CAPM, investors need to have values for the factors contained in the model.
The risk-free rate of return
In reality, there is nothing of the sort as a risk-free resource. Short-term government debt (for example, Depository bills) is a moderately protected investment, is utilized as a satisfactory substitute for the risk-free asset or resource.
However, government debt of different periods will have additional returns, confusing the issue of which is the correct rate to use.
The market risk premium
The market risk premium is also referred to as the equity risk premium. This is the difference between the average return on the capital market and the risk-free rate of return. It addresses the additional return needed for putting investment into equity instead of putting investment into free-of-risk assets.
For a short period, share prices can fall and increase, leading to a negative average return. To smooth out such short-term changes, a time-smoothed moving average analysis can be carried out over more extended periods, often several decades.
Beta
Beta values are found using regression analysis. They intend to compare the returns on a share with the returns on the capital market. The beta incentive for UK organizations traded on the UK capital market can be promptly found on the web.
Formula:
This is the basic formula to find out the required return.
Required return = Risk-free return + Risk premium
This can be further expanded as:
Required return = Risk-free return + (relative level of systematic risk x market risk premium for a specific investment)
Key Points relating to (relative level of systematic risk x market risk premium for a specific investment):
- The overall average return on the market (written as Rm) paid by the stock market more than the risk-free rate (Rf) must represent a fair risk premium for systematic risk.
- The portion of the premium an investor requires relies upon the risk of their investment.
So, the formula becomes:
E(r)i = Rf + Be(E(rm) – Rf)
where:
E(r); = expected return on investment “i” (often expressed as the required return) Rf = risk-free rate of return
E(rm) = the expected average return on the market. This is also shown as Rm.
(E(rm) – Rf) = equity risk premium (also called as average market risk premium)
Be = systematic risk of investment “i” compared to the market. Thus, the amount of the premium needed.
If βe is missing, you can use:
Assets = Capital + Liabilities
Assets = Equity + Debt
Beta Asset = Beta Equity + Beta Debt
Βa = βe + βd
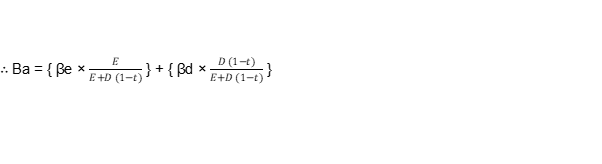
t = tax rate
E = market value of equity
D = Market value of debt
Assumptions:
CAPM has a base, and it’s based on the assumptions given below:
● perfect capital market.
● well-diversified investors.
● non-restricted lending at the risk-free rate of interest.
It is essential to be aware of the assumptions mentioned above. Also, consider the reasons why they can be criticized.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CAPM:
Advantages of CAPM:
The four main advantages of the Capital Asset Pricing Model are as follows:
- It provides a market-based relationship between risk and returns and an assessment of security risk and rates of return given that risk.
- It shows why just systematic risk is significant in this relationship.
- It is probably the best technique for assessing a stated organization’s expense of value capital.
- It gives a premise to set up risk-adjusted discount rates for capital venture projects.
Disadvantages:
The three main disadvantages of CAPM are that:
- It is less valuable if investors are undiversified.
- It also ignores the tax situation of investors.
- The actual data inputs are estimates and may be hard to obtain.
Example:
To help you better understand the CAPM, we’ve written an example below:
The rate on government securities is 15 %, while the market return is 19%.ABC Ltd has the following balance sheet extract.
Ordinary shares (@ $ 0.2/ shares) = $2,000
15% debentures = $3,000
Relevant Notes:
Asset beta is 1.2
Debts are trading @ $120/ $100 nominal, and they can be assumed risk-free
The current share price is $ 1.5/shares
The tax rate is 30%
Required:
E(r)i under CAPM
Solution:
Required return = Risk-free return + (relative level of systematic risk x market risk premium for a specific investment)
E(r)i = Rf + Be(E(rm) – Rf)
E(r)i = 15% + 1.40 (19% – 15%)
E(r)i = 20.6%
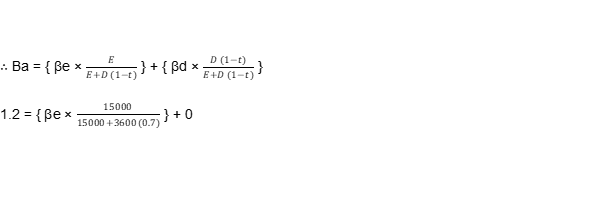
1.2 = βe × 0.85
βe = 1.40
Conclusion:
Capital Assets Pricing Model is abbreviated as CAPM. This model is used to show the relationship between the expected returns and the risk of investing. It has a specific formula that organizations use to calculate their capital asset pricing model.
Comments
Post a Comment
We will appreciate it, if you leave a comment.